Batch fuel forklift production line plant
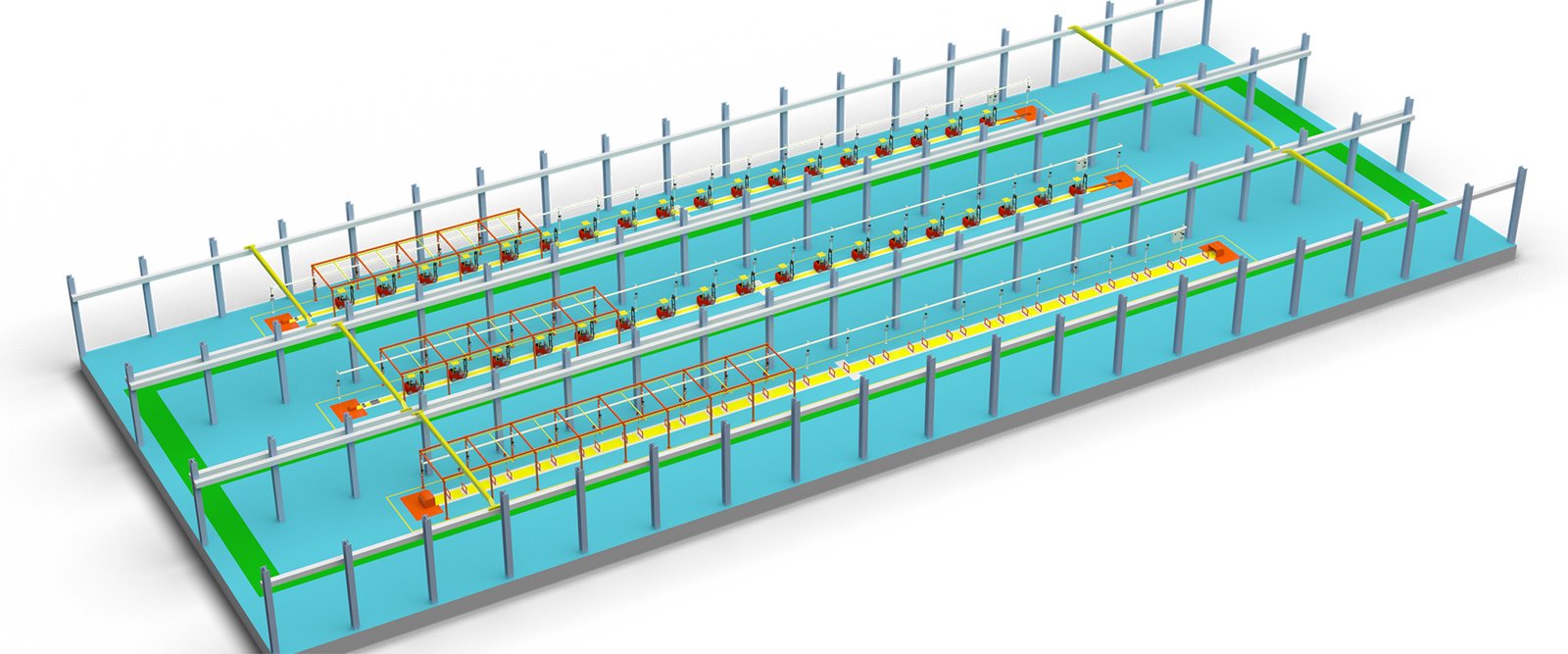
The fuel forklift production line is an industrial system specifically designed for the manufacturing of fuel-powered forklifts, encompassing a multi-stage process. Initially, raw materials such as steel and components are procured and stored. Then, the materials proceed to the cutting and forming stage, where steel is cut to size and shaped into the main structural parts of the forklift. Following this, these parts are welded or assembled into the forklift’s frame and body.
In the painting workshop, the forklift frames undergo cleaning, phosphating, and painting to provide rust prevention and an aesthetic appearance. Subsequently, key components such as the engine, hydraulic system, electrical system, and transmission are installed onto the forklift. The final assembly stage involves the installation of seats, consoles, tires, and other accessories.
During the quality control phase, each forklift undergoes rigorous testing and inspection to ensure its performance and safety meet the standards. Finally, the tested and qualified forklifts are packaged and prepared for shipment to customers. The entire production line is a highly automated and integrated process aimed at ensuring production efficiency and product quality.
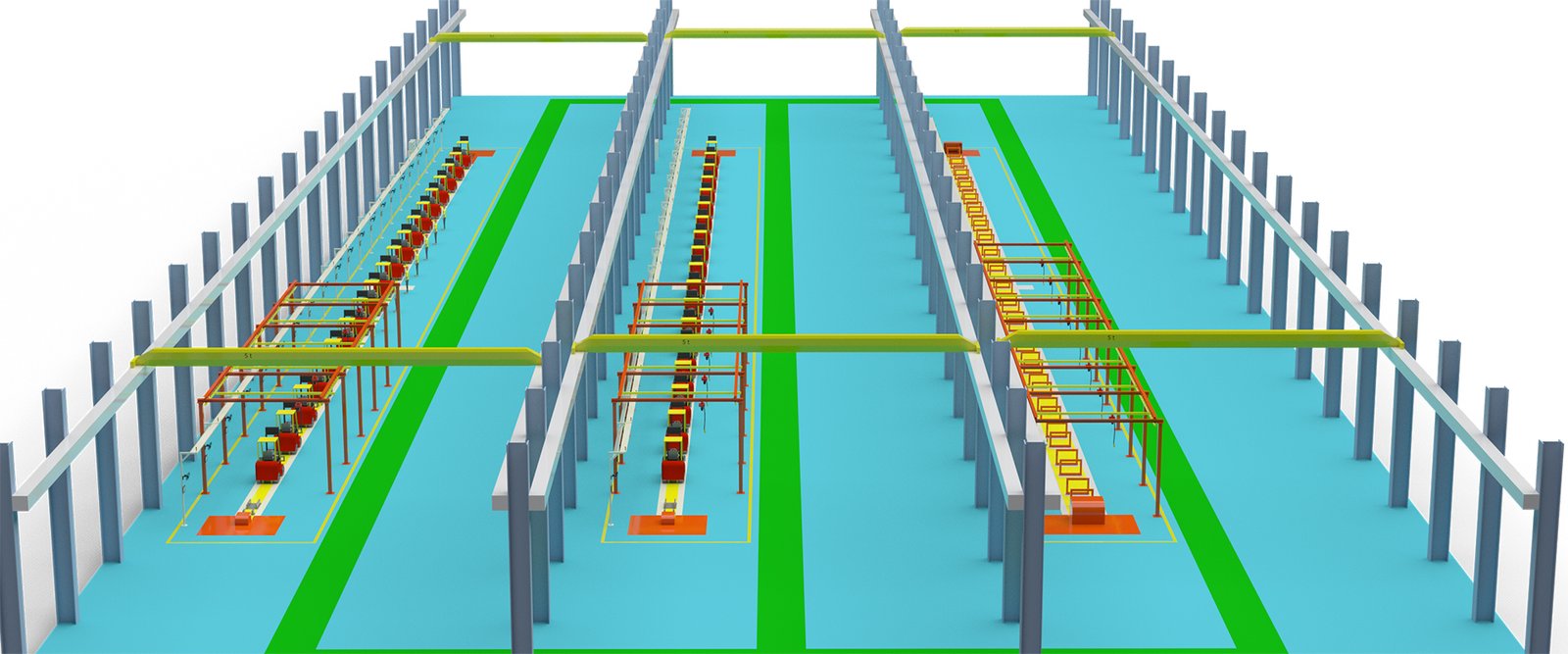
The main production process of fuel forklifts involves several key steps, and each step is typically supported by specialized automated production line equipment. Here’s an overview of the process and the corresponding equipment:
- Material Preparation:
- Equipment: Material handling systems, storage racks, and cutting machines.
- Process: Raw materials such as steel sheets and tubes are stored and prepared for the next stages.
- Cutting and Forming:
- Equipment: Laser cutters, plasma cutters, press brakes, and robotic cutting systems.
- Process: The raw materials are cut to the required dimensions and shapes for the various components of the forklift.
- Welding and Assembly:
- Equipment: Automated welding robots, assembly lines, and fixtures.
- Process: The cut parts are welded together to form the main structure of the forklift, including the frame and body.
- Painting and Finishing:
- Equipment: Automated painting lines, powder coating systems, and curing ovens.
- Process: The welded frame is cleaned, primed, painted, and then cured to achieve a durable and corrosion-resistant finish.
- Component Installation:
- Equipment: Automated assembly lines, robotic arms, and specialized tooling.
- Process: Key components such as the engine, hydraulic system, electrical system, and transmission are installed.
- Final Assembly:
- Equipment: Assembly lines with conveyor systems, robotic assembly systems, and quality inspection stations.
- Process: The final assembly of the forklift includes the installation of seats, control consoles, tires, and other accessories.
- Testing and Quality Control:
- Equipment: Test benches, dynamometers, and automated inspection systems.
- Process: Each forklift is tested for performance, safety, and compliance with specifications.
- Packaging and Shipping:
- Equipment: Packaging machines, palletizers, and forklifts for loading.
- Process: The finished forklifts are packaged, palletized, and prepared for shipping to customers.
Each of these stages is crucial for ensuring the quality and efficiency of the production process, with automation playing a significant role in streamlining operations and reducing manual labor.
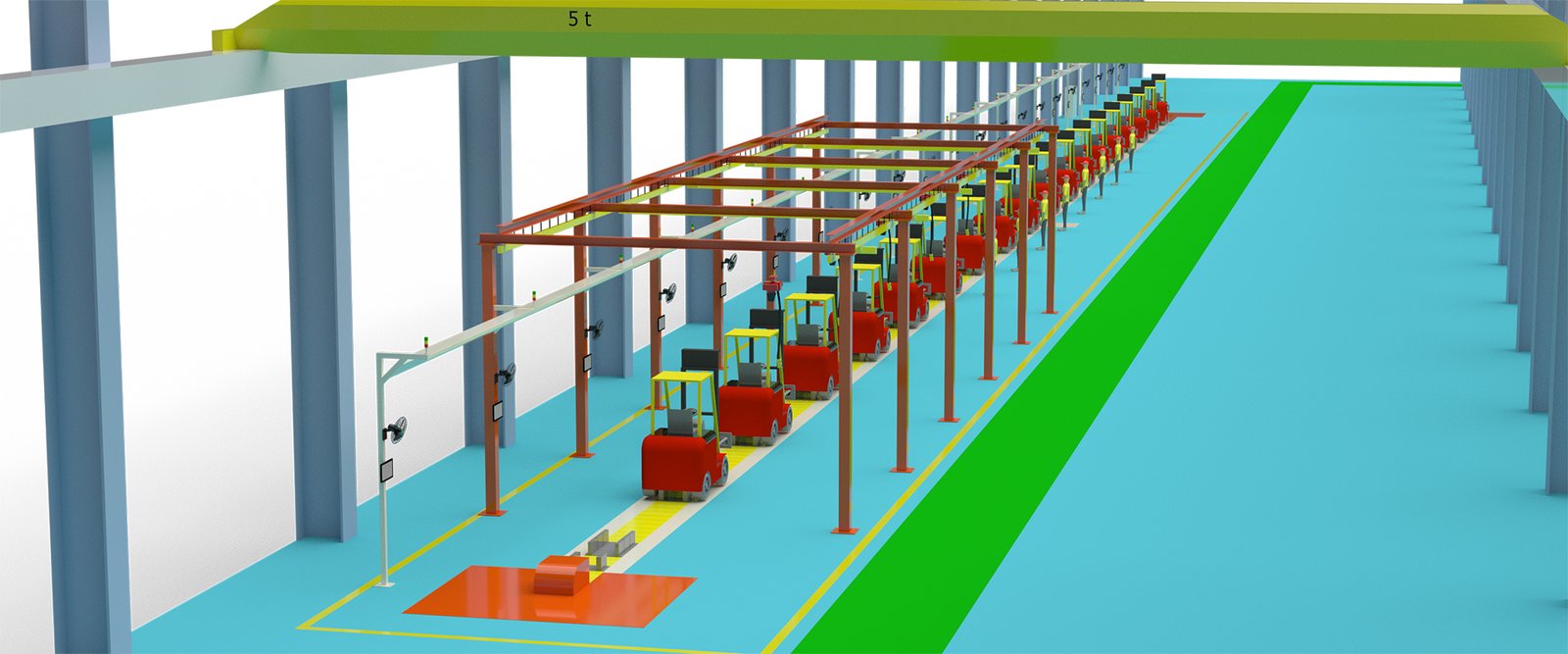

In the production process of fuel forklifts, automated production line equipment enhances production efficiency and product quality in the following ways:
- Reduce manual operations: Automated equipment decreases reliance on manual operations, reducing production defects caused by human errors.
- Increase production speed: Automated production lines can continuously operate without being limited by manual rest times, thus accelerating production speed.
- Consistency and repeatability: Automated equipment can perform tasks with consistent precision and repeatability, ensuring uniform quality standards in every production step.
- Reduce material waste: Precise cutting and forming equipment can reduce material waste and improve material utilization.
- Quality control: Automated inspection and testing equipment can monitor product quality in real-time during the production process, identifying and addressing issues promptly.
- Flexibility and scalability: Automated production lines can be flexibly adjusted according to production needs and are easily expandable to accommodate different production scales.
- Reduce work-related accidents: Automated equipment reduces the time workers spend in hazardous environments, lowering the risk of work-related accidents.
- Data tracking and analysis: Automated systems can collect and analyze production data, helping managers optimize production processes and improve efficiency.
- Reduce production costs: Although the initial investment may be high, automated systems can reduce labor and material waste costs in the long run, thus lowering overall production costs.
- Improve product consistency: Automated production lines ensure that the production process for each forklift is the same, thereby enhancing the consistency and reliability of the products.
- Environmental control: In processes such as painting and welding, automated equipment can operate in controlled environments, reducing environmental impact.
- Maintenance and upkeep: Automated equipment often comes with self-diagnostic and maintenance systems, which can reduce downtime and improve the efficiency of equipment usage.
Through these methods, automated production line equipment not only increases the production efficiency of fuel forklifts but also ensures the quality and consistency of the products, thereby enhancing the competitive edge of the enterprise in the market.
