General-purpose overhead conveying line for vehicle assembly
The general-purpose overhead conveyor line is core logistics equipment for automobile assembly, featuring three-dimensional space utilization and flexible adaptation to high-low stations. Its main types include EMS, FDS, overhead chain conveyor and T.T.S, each with distinct load capacities and application scenarios. It boasts high flexibility, stability and efficiency, adapting to multi-model mixed assembly, and will develop towards intelligence, energy conservation and higher adaptability in the future.
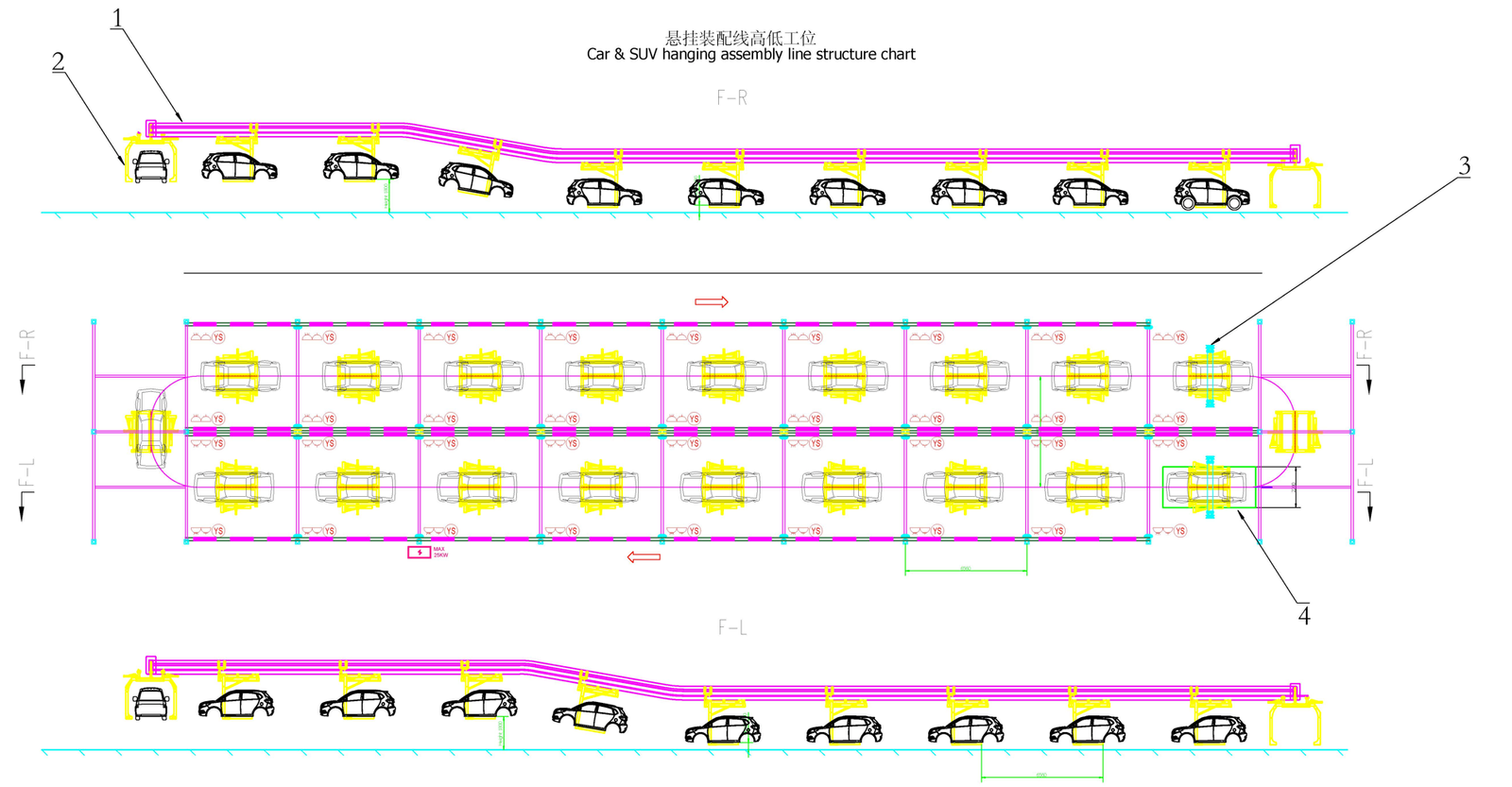
General-Purpose Overhead Conveyor Line for Automobile Assembly
The general-purpose overhead conveyor line for automobile assembly is a core logistics conveying equipment in the automobile whole vehicle and parts assembly production line. Its core advantage is the three-dimensional utilization of production line space, avoiding cross-interference between ground equipment and personnel movement lines. It realizes the continuous, accurate and efficient transfer of automobile body-in-white, interior parts, chassis assemblies, powertrain assemblies and other materials/workpieces between different assembly stations. It is suitable for the flexible assembly needs of multiple models such as passenger cars and commercial vehicles. At the same time, it can be seamlessly connected with ground conveyor lines, robot assembly workstations and testing equipment, making it an important part of the intelligent automobile manufacturing production line. This type of conveyor line can be designed with a height-adjustable station adaptation structure according to the requirements of the assembly process, flexibly matching the operation height of different processes and greatly improving the convenience and efficiency of assembly operations. The following is a detailed introduction from the aspects of core types, structural characteristics, technical parameters and high-low station adaptation design:
I. Core Types and Detailed Technical Characteristics
1.1 EMS Electric Monorail Conveyor System
EMS (Electric Monorail System) is the most widely used overhead flexible conveyor line in automobile assembly. It is composed of overhead monorail track, independent electric trolleys (EMS trolleys), power supply system, control system, positioning device, merging and diverging device, etc. All trolleys are centrally controlled by PLC + independently driven, which can realize independent operation of single trolley and grouped operation of multiple trolleys, adapting to the different needs of “single-piece flow” and “batch flow” in automobile assembly.
1. Structure and Operation Characteristics: The track is modularly spliced with aluminum alloy or section steel, and can be designed with horizontal turning, uphill and downhill, circular bypass and other paths according to the production line layout. The trolley is connected with the workpiece through a suspended spreader, with its own frequency conversion drive system, and the running speed can be steplessly adjusted; it has the functions of automatic merging and diverging, overhead temporary storage and precise positioning, and can start, stop and translate the trolley at any station to meet the mixed-line assembly of multiple models.
2. Technical Parameters: The load capacity ranges from 30kg to 1000kg (light models are suitable for interior parts and small assemblies, heavy models are suitable for the front/rear section of the body-in-white), the running speed is 60-250m/min (empty cars return at high speed, heavy cars assemble at low speed), the positioning accuracy can reach ±1mm (equipped with laser/magnetic grid positioning device), the climbing capacity is ≤15°, which is suitable for the interior assembly of the final assembly workshop and the workpiece transfer before chassis assembly.
3. Application Scenarios: It is the core conveying link of the automobile final assembly line, which can connect the overhead pre-assembly stations of seats, instrument panels, air conditioning systems and other interior parts, and also realize the transfer of the body-in-white between different assembly areas. It is the first choice for flexible production of multiple models.
1.2 Friction Drive System (FDS)
The friction drive system is a continuous overhead conveyor line. It mainly relies on the friction force between the “friction wheel – trolley connecting rod” to realize workpiece conveying. It is composed of overhead track, friction drive device, conveying trolley, spreader, tensioning device and positioning mechanism. The drive device is arranged beside the track at a fixed pitch, and the friction wheel is driven by the motor to rotate, contacting the friction surface on the side of the trolley to drive the trolley and the workpiece to move continuously along the track. There is no traction chain/belt, which belongs to the “non-contact” drive.
1. Structure and Operation Characteristics: The track is mostly a section steel welding structure with high overall rigidity, suitable for heavy-load conveying; the conveying trolley is a standardized module, mostly adopting a three-link/four-link structure, and there is no rigid connection between the trolleys, which can realize small spacing adjustment, stable operation without impact and low noise (≤65dB); the drive device can be started and stopped independently, and the trolley can run at low speed or pause at local stations to meet the station assembly operation.
2. Technical Parameters: The load capacity is 500kg-3000kg (focusing on heavy-load conveying, suitable for the overall transfer of the body-in-white), the running speed is 0.5-30m/min (mainly low-speed continuous operation, suitable for the slow-paced operation of assembly stations), the positioning accuracy is ±2mm, the climbing capacity is ≤12°, and the track can realize horizontal turning with a maximum R5m, adapting to the compact layout of the production line.
3. Application Scenarios: The rear section of the automobile painting workshop and the body-in-white conveying of the final assembly workshop are suitable for assembly processes with high requirements on operation stability, heavy load and continuity. They can cooperate with robots for body welding, gluing, appearance inspection and other operations.
1.3 Overhead Chain Conveyor
The overhead chain conveyor is a classic type of traditional overhead conveyor line, which belongs to a chain-driven continuous conveying equipment. It is composed of traction chain, overhead track, carriage, spreader, drive device, tensioning device, tensioning device and safety protection device. It mainly drives the traction chain to circulate through the motor, the carriage is fixedly connected with the chain, and the spreader is suspended on the carriage to drive the workpiece to run synchronously along the track. It has a simple structure and high reliability, and is the preferred choice for “low-cost and large-flow” conveying in automobile assembly.
1. Structure and Operation Characteristics: The track is divided into straight section, turning section and climbing section, which is made of channel steel, I-steel and other profiles, and can realize 360° turning and uphill/downhill in space with flexible layout; the traction chain is a plate chain/roller chain with strong bearing capacity, and the carriage is connected with the track through rollers with small friction resistance; an accumulation section can be set beside the track according to the process requirements to realize the temporary storage of workpieces at the station, adapting to the beat difference of the assembly process.
2. Technical Parameters: The load capacity is 50kg-2000kg, the running speed is 0.3-25m/min (low-speed continuous operation, suitable for manual assembly stations), the minimum radius of horizontal turning is R1.5m, the minimum radius of vertical turning is R3m, the climbing capacity is ≤30° (light load condition), the positioning accuracy is ±5mm, which is suitable for medium-light load and fixed-beat assembly processes.
3. Application Scenarios: Automobile parts pre-assembly lines (such as separate assembly of doors, hoods and fenders), small parts conveying in the final assembly workshop (such as tires, batteries and wire harnesses), and also can be used for overhead conveying and temporary storage of finished vehicles after the completion of the whole vehicle assembly.
1.4 T.T.S Twin Trolley System
T.T.S (Twin Trolley System) is a high-end modular overhead conveyor line, specially designed for the needs of heavy load, high precision and high flexibility in automobile manufacturing. It is composed of overhead traveling guide rail, unpowered double trolley, toothed belt drive device, traversing device, rotary positioning device and spreader system. The drive device is installed on the guide rail, and the two driven parts of the double trolley are driven by the toothed belt to realize the synchronous operation of the trolley. Its core advantages are “no traction chain, traversable and 360° rotatable”.
1. Structure and Operation Characteristics: It adopts the design of double trolley + double guide rail, which has a large contact area between the trolley and the workpiece and strong bearing stability; the drive system is synchronous drive with toothed belt, with high running precision and no slip, which can realize independent operation and grouped operation of the trolley; it is equipped with a special traversing device, which can realize the transverse transfer of workpieces between different guide rails, greatly improving the flexibility of the production line layout; the trolley can be equipped with a rotating spreader to realize 360° rotation of the workpiece, meeting the multi-angle operation of the assembly station.
2. Technical Parameters: The load capacity is 1000kg-5000kg (can carry the complete body-in-white and part of the chassis assembly), the running speed is 5-40m/min, the positioning accuracy is ±0.5mm (equipped with a servo positioning system), the maximum traversing distance can be 10m, the climbing capacity is ≤10°, which is suitable for the core processes of the automobile final assembly workshop.
3. Application Scenarios: The chassis assembly, overall body-in-white assembly of the automobile final assembly line and the high-end production line of mixed-line production of multiple models. It is the core conveying equipment of the intelligent assembly line of luxury cars and new energy vehicles, and can be seamlessly connected with AGV and robot assembly workstations.
II. High-Low Station Adaptation Design of Overhead Conveyor Line
In the process of automobile assembly, different processes have great differences in the required operation height (for example: chassis assembly requires low-position operation, interior assembly requires medium-position operation, and roof component assembly requires high-position operation). The general-purpose overhead conveyor line for automobile assembly realizes flexible adaptation of high and low stations through three core methods: track high-low section design, spreader lifting adjustment and trolley station lifting, while ensuring the stability of the conveying process and the convenience of operation. The detailed design points are as follows:
2.1 Modular Design of Track High-Low Sections
This is the basic high-low station adaptation method of the overhead conveyor line. It mainly realizes that the workpiece naturally enters the stations of different heights along the track with the conveying trolley through the segmented elevation design of the overhead track. No additional lifting device is needed, the structure is simple and the cost is low. It is suitable for the processes with fixed beat and unchanged operation height.
1. Design Principles: The high and low sections of the track are connected by a gentle slope transition section, and the climbing angle of the transition section is ≤15° (≤10° for heavy-load conditions) to avoid tilting and shaking of the workpiece during lifting; the track elevation difference is designed according to the station operation requirements, and it is usually adapted to three operation heights: low position (0.5-1.2m), medium position (1.2-1.8m) and high position (1.8-3.0m).
2. Application Scenarios: Small parts pre-assembly stations (medium position), roof rack/sunroof assembly stations (high position), chassis workpiece transfer stations before tire assembly (low position), suitable for continuous conveyor lines such as overhead chain conveyors and FDS friction drive systems.
2.2 Spreader Lifting Adjustment Design
By setting a liftable spreader between the conveying trolley and the workpiece, the vertical height adjustment of the workpiece under the same track elevation is realized. It is the most flexible high-low station adaptation method of the overhead conveyor line. The lifting spreader is composed of an electric push rod/hydraulic cylinder, guide rod, locking device and spreader frame. It can realize automatic lifting and precise positioning through PLC control, and the lifting height can be steplessly adjusted according to the process requirements.
1. Design Characteristics: The lifting stroke of the spreader is generally 0.3-2.0m, the lifting speed is 0.05-0.2m/s (low speed and stable to avoid workpiece shaking), the guide rod is equipped to ensure the lifting verticality, the locking device can fix the spreader at any height, and the positioning accuracy is ±1mm; the lifting spreader is of modular design, which can be replaced according to the workpiece type to adapt to the mixed-line assembly of multiple models.
2. Core Advantages: The same conveying track can be matched with multiple assembly stations of different heights without changing the track layout, which greatly improves the flexibility of the production line; the workpiece can realize “precise lifting + pause” at the station, meeting the multi-angle and multi-height operation needs of manual assembly or robot assembly.
3. Application Scenarios: The core adaptation method of EMS electric monorail system and T.T.S twin trolley system, which is suitable for the core processes such as interior assembly, chassis assembly and powertrain assembly of the automobile final assembly workshop. For example: after the instrument panel is assembled on the body-in-white at the medium position, the spreader descends to the low position, cooperates with the robot to complete the chassis assembly, and then rises to the medium position to complete the seat assembly.
2.3 Trolley Station Lifting Design
For heavy-load and large-size workpieces (such as complete body-in-white and commercial vehicle cab), a station-specific trolley lifting device is designed. After the conveying trolley runs to the designated station, the lifting platform of the station lifts the trolley and the workpiece as a whole to realize vertical height adjustment. The conveying track remains horizontal, avoiding problems such as track deformation and trolley slipping when the heavy-load workpiece climbs on the track.
1. Design Characteristics: The lifting platform adopts a hydraulic drive + scissor structure, with strong bearing capacity (more than 5000kg), the lifting stroke is 0.5-1.5m, and the lifting is stable without impact; it is equipped with a trolley positioning device to ensure the precise fixation of the trolley on the lifting platform and avoid the trolley shifting during the lifting process; the lifting platform is linked with the control system of the conveyor line to realize the automatic process of “arrival – lifting – assembly – reset – conveying” of the trolley.
2. Application Scenarios: The body-in-white conveying of commercial vehicle final assembly lines and new energy vehicle heavy-duty truck assembly lines, suitable for heavy-load conveyor lines such as FDS friction drive systems and T.T.S twin trolley systems. For example: after the commercial vehicle cab is conveyed to the chassis assembly station by the horizontal track, the lifting platform lowers the cab to the low position, completes the assembly with the chassis, and then rises to the horizontal track to continue conveying to the subsequent assembly stations.
2.4 Supporting Design for High-Low Station Adaptation
1. Safety Protection: Safety guardrails, photoelectric sensors and emergency stop buttons are set at the transition sections of high and low stations and lifting stations to prevent personnel from entering dangerous areas; during the workpiece lifting process, an anti-falling device is set to avoid accidental falling of the workpiece.
2. Movement Line Planning: The high and low stations of the overhead conveyor line are strictly separated from the movement lines of ground personnel and AGVs. A protective net is set under the high-position track to prevent debris on the workpiece from falling, and sufficient personnel operation space (≥0.8m) is reserved at the low-position stations.
3. Synchronous Control: The lifting action of the high and low stations, the operation of the conveyor line and the assembly action of the robot are linked and controlled by PLC to ensure the beat synchronization of each process and avoid production line jamming.
III. Core Advantages and Application Requirements of General-Purpose Overhead Conveyor Line for Automobile Assembly
3.1 Core Advantages
1. High Space Utilization: It occupies the production line space in three dimensions, releases the ground area, which can be used to arrange AGVs, robot workstations, material racks, etc., and optimizes the production line layout.
2. High Flexibility: Modular design, which can flexibly adjust the track layout and the number of stations according to the production line capacity expansion and model replacement, adapting to the mixed-line assembly of multiple models.
3. Stable and Reliable Operation: All core components are designed in standardization and serialization, with low failure rate, convenient maintenance and 24-hour continuous operation.
4. High Assembly Efficiency: Through the high-low station adaptation design, it matches the operation height of different processes, reduces the invalid operations such as bending and lifting of personnel, improves the assembly efficiency, and can be seamlessly connected with automatic equipment to realize the intelligence of the assembly process.
3.2 Application Requirements
1. Plant Conditions: The plant is required to have sufficient clear height (generally ≥6m) and roof bearing capacity (designed according to the load capacity of the conveyor line, generally ≥500kg/㎡) to ensure the installation and operation safety of the overhead track.
2. Process Matching: The type of conveyor line should be reasonably selected according to the process beat, workpiece weight and operation height of automobile assembly. For example: passenger car production lines with high flexibility requirements prefer EMS and T.T.S systems, and low-cost, continuous parts pre-assembly lines prefer overhead chain conveyors.
3. Control System: A centralized PLC control system should be built to realize the linkage between the conveyor line and robots, AGVs and testing equipment. At the same time, a production line monitoring system should be equipped to real-time monitor the operation status of the conveyor line and the station beat, so as to realize the intelligent management of the production line.
IV. Development Trends
With the transformation of automobile manufacturing towards intelligence, flexibility and new energy, the general-purpose overhead conveyor line for automobile assembly is also developing towards high flexibility, high precision, intelligence and energy saving:
1. Flexibility Upgrade: Adopt the global independent trolley design to realize the independent and precise control of each trolley, adapt to the mixed-line assembly of more models, and the track layout adopts the detachable and modifiable aluminum alloy modular structure to reduce the production line transformation cost.
2. Intelligence Upgrade: Equipped with 5G, Internet of Things and visual recognition technologies to realize intelligent scheduling of trolleys, full-process traceability of workpieces and intelligent detection of stations. At the same time, AI algorithms are equipped to optimize the operation path of the conveyor line and improve the production line beat.
3. Energy Saving Upgrade: Adopt frequency conversion drive and energy recovery technologies to reduce the energy consumption of the conveyor line. For example: the kinetic energy of the trolley when going downhill is converted into electric energy for recycling, and the drive device adopts high-efficiency energy-saving motors to realize green production.
4. High-Low Station Adaptation Upgrade: Combined with ergonomics, design a flexible operation height that can be automatically adjusted according to the height of the operator, and cooperate with collaborative robots to realize automatic assembly of high and low stations, further improving assembly efficiency and operation comfort.
