Ground pits and reinforced concrete foundations for conveyor line installation
This article details the design and construction of pits and reinforced concrete foundations for conveyor line installation. Pits accommodate drive units, tensioning devices, and maintenance access, with types ranging from shallow trenches to deep excavations requiring ventilation and drainage. Foundation options include spread footings, strip foundations, raft slabs, and pile foundations, selected based on load requirements and soil conditions. Key considerations cover structural safety, load calculations, vibration isolation, and construction precision, with strict acceptance standards ensuring proper alignment and long-term operational stability of conveyor systems.
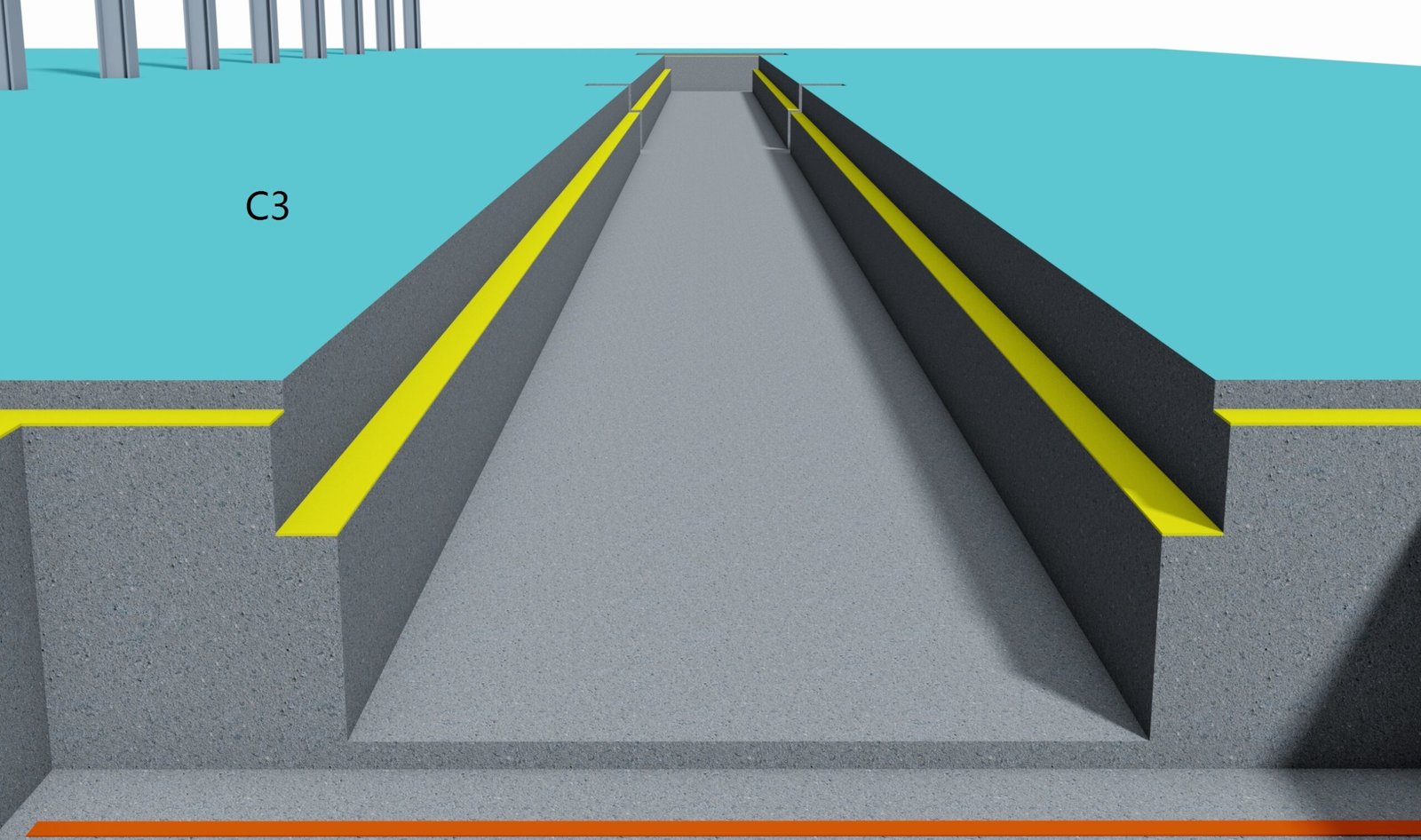
I. Conveyor Line Pits
1. Definition and Function
A pit/trench is a man-made space excavated below ground level, used for:
- Installing conveyor line drive units (motors, gearboxes)
- Arranging conveyor tensioning devices (gravity take-up, screw take-up)
- Accommodating conveyor belt return sections (sunken layout)
- Housing electrical control cabinets and conduit passages
- Providing maintenance access for personnel
2. Types of Pits
| Type | Application | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Deep pit | Large-inclination belt conveyors, hoists | Depth 2-5m, requires ladders, ventilation, drainage |
| Shallow pit | Horizontal conveyor tensioning devices | Depth 0.5-1.5m, simple waterproofing |
| Elongated pit | Long-distance belt conveyor take-up units | Length up to 10-30m, settlement consideration required |
| Equipment pit | Drive stations, bend stations | Integrated design with equipment foundations |
3. Design Requirements
Structural Safety
- Side walls require earth pressure calculations, support structures when necessary
- Depths exceeding 2m require design according to excavation engineering standards
- High groundwater levels require waterproof curtains or well-point dewatering
Functional Requirements
- Reserve equipment lifting openings or embedded lifting rings
- Install sump pits and automatic drainage pumps (prevent water accumulation)
- Configure ventilation facilities (forced ventilation when depth >3m)
- Maintenance lighting and electrical safety (explosion-proof requirements where applicable)
Dimensional Allowances
- Minimum 800mm clear space around equipment (maintenance access)
- Top cover load capacity ≥5kN/m² (forklift trafficable)
- 100mm thick C15 concrete blinding layer at pit bottom
II. Reinforced Concrete Foundations
1. Foundation Type Selection
| Foundation Type | Applicable Conditions | Construction Key Points |
|---|---|---|
| Spread footing (isolated foundation) | Single frames, column supports | Stepped or tapered, embedment depth ≥0.5m |
| Strip foundation | Continuous multi-span conveyor frames | Longitudinal arrangement along conveyor line, width ≥support spacing |
| Raft foundation | Soft soil, heavy-duty conveyor lines | Monolithic thick slab, thickness 300-500mm |
| Pile foundation | Backfill, weak soil layers | Precast or cast-in-place piles, bearing capacity verification |
| Equipment foundation block | Drive units, tension pulleys | Mass ≥3-5 times equipment weight (anti-vibration) |
2. Design Calculation Essentials
Load Combinations
- Permanent loads: structural self-weight, equipment weight, prestress
- Variable loads: conveyed material weight, impact loads, wind loads
- Accidental loads: seismic action (areas above intensity 7)
Bearing Capacity
- Modified characteristic value of subgrade bearing capacity ≥1.2 times base pressure
- Weak underlying layer verification (when weak soil layers exist)
- Foundation deformation calculation (differential settlement ≤0.002 times span)
Reinforcement
- Bottom slab main bars diameter ≥12mm, spacing ≤200mm
- Reinforcing mesh around equipment anchor bolts
- Distribution bars at foundation top to prevent cracking
3. Construction Details
Embedded Parts
- Anchor bolts: Q235B or 45# steel, embedment depth ≥20d (d = bolt diameter)
- Embedded steel plates: thickness ≥10mm, flatness ≤3mm/m
- Anchor bars: HRB400 grade, anchorage length ≥40d
Vibration Isolation
- Separation between drive unit foundation and conveyor frame foundation (vibration joint ≥50mm)
- Rubber pads or spring isolators at heavy impact locations
- Pile foundations for high-vibration equipment (pile tip into rock or dense soil layer)
Special Treatments
- Frost-susceptible areas: foundation embedment below frost line by 0.25m
- Corrosive environments: concrete grade ≥C35, increased cover thickness
- Explosion-proof areas: anti-static grounding treatment on foundation surface
III. Key Construction Procedures
1. Pit Excavation and Support
- Slope excavation (when soil conditions are good) or steel sheet pile support (near existing structures)
- Over-excavated portions backfilled with sand-gravel compaction, strictly prohibited to leave loose fill
- Foundation trench inspection to verify soil properties match geotechnical reports
2. Reinforcement Work
- Concrete cover spacers spacing ≤1m, bottom cover ≥40mm
- Anchor bolt positioning using定型formwork, deviation ≤2mm
- Reinforcement mesh lap length ≥35d, staggered joints by 50%
3. Concrete Placement
- Continuous placement in one operation, layer thickness ≤500mm
- Equipment foundations reserved for secondary grouting layer (thickness 50-100mm)
- Curing period ≥7 days, winter construction insulation measures
4. Embedded Parts Accuracy Control
- Anchor bolt center distance deviation ≤±2mm
- Embedded steel plate top elevation deviation ≤±3mm
- Levelness deviation ≤1/1000
IV. Acceptance Standards
| Inspection Item | Permissible Deviation | Inspection Method |
|---|---|---|
| Foundation coordinate position | ±20mm | Theodolite |
| Foundation top elevation | ±10mm | Level |
| Embedded anchor bolt center distance | ±2mm | Steel tape |
| Embedded anchor bolt projection length | +20/0mm | Steel tape |
| Foundation surface flatness | ≤5mm/2m | 2m straightedge |
